What Will 5G Mean for Displays and AR/VR Devices?
Technology industry prognosticators have been saying that 2020 will be a big year for 5G networks. It looks like they’re right, as a flurry of rollouts have taken place around the globe, starting with a handful of high-profile (if limited) carrier launches in 2019, and more coming almost weekly. Mobile industry organization GSMA reports that 5G is now live in 24 markets worldwide and predicts that 20% of global connections will be on 5G by 2025.1

Tower technicians make final antenna alignments prior to Sprint’s 5G testing in Chicago in February 2019, an early milestone for the commercialization of 5G using 2.5 GHz and Massive MIMO. A speed test at the time showed 422 Mbps. (Image: © Wireless Estimator)
Benefits of 5G
Shorthand for “fifth generation,” 5G cellular network technology (specifically 5G NR) promises a major leap forward in broadband speed and performance. As summarized by the IEEE, “the three key benefits of 5G networks are:
- Much higher data rates (1-20 Gbit/s), enabling consumers to download content more quickly.
- Much lower latency (1 ms), allowing users to experience less delay/lag when requesting data from the network—a latency of milliseconds, imperceptible to humans.
- Increased capacity as the network expands.”2
5G networks are expected to improve internet reliability and speed: average download speeds of around 1GBps are expected to be the norm.3 “One important benefit of the technology is its ability to greatly reduce latency, or the time it takes for devices to communicate with one another. That will be important for the compatibility of next-generation devices like robots, self-driving cars and drones.”3 These devices are dynamic—they move in real time in the real landscape—so millisecond response time is critical for being able to operate safely, respond to external stimuli, and avoid colliding with other moving objects.
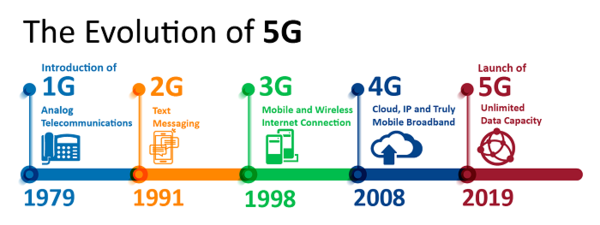
Development of telecommunications network technology up to the present fifth generation (5G). (Image Source)
The Potential of 5G
The anticipation for 5G has been building for several years across multiple industries because of its potential widespread impact: it will expand the universe of IoT and provide the infrastructure needed to carry huge amounts of data, which will enable connectivity that hasn’t existed before. “5G will enable billions of new connections with speed and security. It will connect everything to everything (X2X), acting as a critical enabler for Massive IoT, Connected Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs), remote critical control and more. Cars will be connected to the roads and cities they navigate, doctors connected to the medical devices of their patients, and physical infrastructure and assets connected to those tasked with maintaining and managing them.”4
For example, 5G could enable people to enjoy console-quality streaming game services wherever they are, even without Wi-Fi. Travelers could download a movie in seconds before boarding an airplane, and sports fans could achieve fast network and even phone connectivity within a packed stadium.
Beyond entertainment, 5G networks could enable real-time, remote biometric authentication to enhance data security. 5G could also advance applications of ICT Agriculture (information and communication technology in agriculture).5 Medical professionals using 5G devices could diagnose and start directing treatment for patients while they are still in an ambulance on their way to the hospital.6
5G Coming Soon to Phones Everywhere?
With large swaths of the global population now transitioning to working and staying at home in response to the current Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, telecommunications providers are hurrying to roll out and expand 5G networks sooner than scheduled. For example:
- Japanese cell phone carriers had originally planned to launch and promote 5G networks and services in conjunction with the July 2020 Olympic Games in Tokyo. With the games now being delayed, carriers such as KDDI and NTT Docomo are rolling out 5G services as early as the week of April 1. Read more…
- The Chinese government just issued a directive urging municipalities to hasten the building of 5G network capabilities, particularly to construct 5G-enabled smart medical systems. The directive also encouraged the rapid development of 5G applications in AR/VR for both industrial and automotive uses.
5G and the Display Industry
The potential impact of 5G on daily life could be huge as more and more devices, equipment, systems, and vehicles take advantage of its capabilities. However, the impact on the display screens embedded in these devices may be blunted. Display technologies like OLED, microLED, quantum dot and others are already increasing screen resolution and picture quality—although perhaps not enough.
Next-generation 5G-enabled TVs could theoretically stream images with several times more pixels than today’s HD or even 4K TVs can replicate. Some analysts suspect that “while some early adopters will pay a premium price for sets that can display [the images enabled by 5G], extreme levels of definition exceed most people’s visual acuity, so viewers will see little reason to upgrade”7 their display devices.
On the other hand, some experts suggest that 5G will help propel the market for 8K television screens using OLED, microLED, QLED and/or other display technologies.8
In the smartphone market, 5G is already driving the design and release of new phone models from major brands like Samsung and Motorola. 5G’s ability to enhance signal strength and speed, even when a user is in a crowded environment surrounded by other users, is one of the big draws for consumers.

The Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G Phone (Image © Samsung)
Dramatically faster streaming video is another draw for smartphone consumers. Video represents 64% of the roughly 27 exabytes (1 exabyte = 1 million terabytes) of data traffic per month currently, according to Ericsson,9 and is expected to be 74% of the worldwide total traffic of 136 exabytes by 2024.9 And with the enhanced ability to stream video and console-quality gaming content, users are going to expect a highly responsive, high-res screen to match.
5G and AR/VR/MR
The increased bandwidth of 5G is poised to give augmented-, virtual- and mixed-reality (collectively “XR”) devices and applications a boost. The enhanced speed and performance of 5G could be “transformational” for AR in particular, speeding its adoption into the mainstream market.10
AR applications are typically very data intensive: AR devices often have powerful processors, high-resolution cameras, a range of sensors, plus software running concurrently to deliver a real-time experience. 4G networks don’t have the capacity or the low latency to support this data load, which means that, currently, many AR applications are “localized” with a significant portion of processing handled within the hardware device.
With 5G networks, offering 10X or greater improvements in throughput, capacity, and latency, AR applications would be able to offload data-intensive processing to the cloud. AR/MR headsets and smart glasses could become smaller, lighter, more energy efficient, and less expensive, increasing their appeal to mass market consumers.
Increased network capabilities will also give “developers a larger canvas on which to design new experiences,”11 leading to more sophisticated and expansive AR applications integrated with the user’s environment. For example, AR-enhanced live events could be transmitted in real time, and AR experiences could incorporate more haptic feedback to create a new “Tactile Internet.”.11

Concept image of the Vive Photon prototype from HTC, an MR headset still under development, which is planned to use 5G (although the details are still being worked out). As HTC CEO Yves Maitre says: “It’s not reasonable to have a 5G antenna near the brain of customers”11 so the company is looking at options such as connecting to the network via an externa pack or the user’s phone. (Image © HTC Corporation/Vive)
Next-Level Device Performance Demands the Highest Standards in Quality Inspection
To produce the high-performing devices of the 5G era, manufacturers of televisions, phones, AR/VR headsets, and other display devices will require rigorous quality control. Radiant’s ProMetric® Imaging Photometers and Colorimeters provide high-resolution, precision measurement for the backlit and emissive displays of both today and tomorrow.
For OLED, microLED, and other emissive display types, our systems measure at the pixel and subpixel level to detect and correct defects like insufficient brightness, inconsistent color output, and dead or stuck-on pixels. For XR devices like visors and smart glasses, our AR/VR Lens and TT-ARVR™ software offer a solution for lab and production display testing across a full, immersive field of view as seen through the headset—up to 120° horizontal, 80° vertical in a single measurement image. Our scientific and in-line metrology solutions ensure devices are designed and produced to meet manufacturer specifications for brightness, color, contrast, uniformity, clarity or sharpness, focus, and objective visual quality.
As the display industry continues to evolve in response to both consumer demand and technology advancements, Radiant solutions are engineered to measure new visual performance requirements and help you achieve your manufacturing objectives.
CITATIONS
- The Mobile Economy 2020, Report from GSM Association / GSMA Intelligence, March 2020.
- “Three Key Benefits of 5G”, IEEE Innovation at Work, https://innovationatwork.ieee.org/3-key-benefits-of-5g/ (retrieved March 25, 2020).
- McCann, J. et al., “5G: everything you need to know”, TechRadar, Jan 17, 2020.
- “Three Key Benefits of 5G”, IEEE Innovation at Work, https://innovationatwork.ieee.org/3-key-benefits-of-5g/ (retrieved March 25, 2020).
- Haselton, T., “Is 5G Really That Fast”, CNBC Tech, March 2, 2020.
- Iwamura, M., “A New Paradigm Begins with 5G and XR”, presented at SPIE AR, VR, MR Conference 2020, San Francisco, CA, February 3, 2020.
- Nersesian, R., “What Effect Will 5G Have On Our World?”, Forbes, September 30, 2019.
- May, S., “New Screen Technologies and 5G to Drive 8K TV Adoption”, ChannelNews, July 4, 2019.
- Brennesholtz, M., “Displays, Data Traffic and 5G Networks”, Display Daily, published May 2019 (retrieved March 26, 2020)
- Mundy, J., “How 5G could improve augmented reality”, TechRadar, June 1, 2019.
- Robertson, A., “HTC is prototyping an AR headset that looks like sunglasses”, The Verge, Feb 20, 2020.
Join Mailing List
Stay up to date on our latest products, blog content, and events.
Join our Mailing List
