Expected Boom in AR/MR Applications Depends on Device Quality
Uses and potential applications of augmented (AR), virtual (VR), and mixed (MR) reality devices are growing rapidly in industries as diverse as gaming, military, education, transportation, manufacturing, and medicine. The AR/VR-headset and smart-eyewear market is anticipated to reach sales of 81.2 million units worldwide by 2021, growing at the rate of 56.1% (CAGR).1 Market revenues for augmented reality alone are projected to reach $90 billion by 2022, far exceeding the projected VR market segment at just $15 billion.2
The explosive growth of the AR segment can be attributed to the “ubiquity” of augmented applications compared to the “focus” of virtual reality.2 With a virtual reality headset, the user’s entire view is filled with displayed images, creating an immersive experience. This “you are there” experience can block out awareness of and interactions with the real environment—i.e., it focuses the user’s attention entirely on what’s on screen.
By contrast, augmented and mixed reality systems project images or information in front of the user’s eyes while the real-world background remains visible, enabling AR/MR users to receive real-time information like weather updates or text alerts while walking down the street. Often the information on an AR/MR display can be directly related to what the user is viewing in their current environment, for example detailed equipment schematics and instructions displayed in a technician’s view during an on-site repair. In essence, AR/MR can potentially accompany us almost anywhere, a ubiquitous presence at work or in life.

Augmented reality can be used for myriad applications, including industrial training. Image: Carlos Fy [CC BY-SA 4.0]
A Proliferation of Realities
Driving the growth of VR/AR/MR technologies is a multiplicity of potential uses and applications. VR may be associated in the public perception primarily with gaming and entertainment, but it has many applications in areas as diverse as medicine, education, and defense. Nevertheless, AR technology has many more potential applications in a wide range of industrial, enterprise, and consumer settings. The number of AR use cases is vast, spanning almost every realm of human activity from manufacturing and construction to food and fitness. Enterprise applications for AR/VR/MR technologies include:
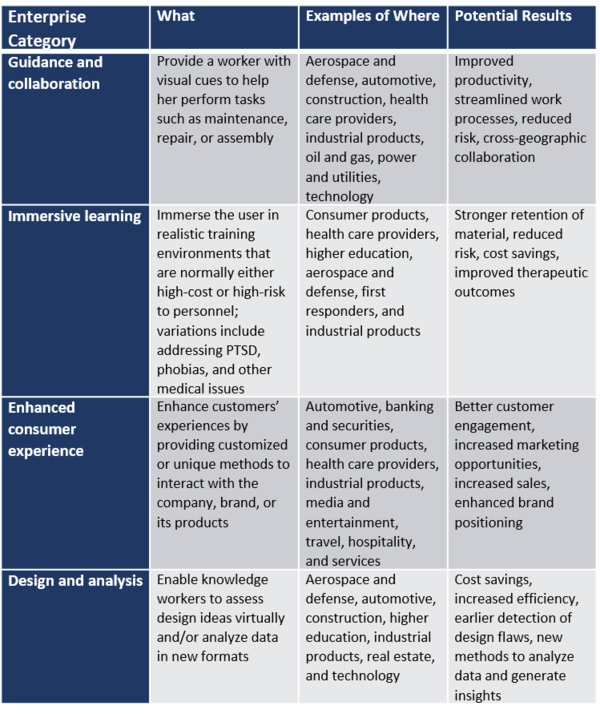
Source: Adapted from Deloitte.
For example, augmented reality could help firefighters save lives. At the scene of a fire, there are limits to what thermal cameras can do to help firefighters see in dark or smoky conditions. A new prototype AR system, called C-Thru, mounts a wearable, augmented reality display inside a standard firefighters’ mask. Developed by Qwake Tech, the system uses a combination of thermal imaging, edge detection, and toxicity sensors to enhance the environment with green outlines of doors, humans, and other elements so firefighters can “see” more clearly.

The C-Thru helmet-mounted AR system (left) and the detailed imaging it can provide to firefighters even in zero-visibility environments (right). Images source: CBS News.
A few other interesting AR applications already in use today include:
- Home Decorating – IKEA has a new home decorating app that uses AR technology to let customers see exactly how furniture items will look in their home. Learn more…
- Navigation – At this year’s CES show, Hyundai demonstrated an AR navigation system using technology from WayRay. Unlike conventional head-up displays, which project images within a small “eyebox” region, this new holographic AR system projects images across the entire windshield, synchronized with real-world objects. Learn more...
- Medical Education – Cleveland Clinic and Case Western Reserve University have teamed up with Microsoft to develop HoloAnatomy, an application for the HoloLens that allows students to visualize and collaborate to learn anatomy. Learn more…
- Consumer Awareness – Since 2007, The Coca-Cola Company has been partnering with World Wildlife Federation on initiatives to help conserve the world’s freshwater resources. They launched an Arctic Home Campaign to raise awareness of the plight of polar bears due to vanishing Arctic ice, and recently created an AR experience at the London Science Museum:
AR Smart Glasses
Despite these recent AR successes, we’re still a distance away from widespread adoption of devices like AR/MR glasses for everyday consumer use. One challenge is the simple matter of form factor (size, shape, and weight) involved in transporting a cluster of information processing technologies on one’s head, which can be a deterrent to everyday use. Clay Bavor, who runs Google’s VR and AR unit, says “several technological breakthroughs will be required to minimize the display and optics” of smart eyewear devices before practical usability can be achieved.
Some of the key development areas in AR/VR technology include advancements in gesture sensing, depth-map sensing, and eye tracking within headsets to enable better varifocal and foveated rendering—in particular, using eye tracking as a vergence tracker so that displayed images can switch from far-field to near-field view as the user changes their focus.
Enabling Precise Measurement for Near-eye Displays
The expanding number applications for headsets and glasses fuels an increasing need to measure AR/VR/MR displays viewed near to the eye—together referred to as near-eye-displays (NEDs)—with methods that can be adapted to the geometries of each different device and various display specifications.
Radiant has developed a display measurement solution specially engineered to measure NEDs, such as those integrated into virtual, mixed, and augmented reality headsets—the AR/VR Lens. The innovative geometry of this lens simulates the size, position, and field of view of the human eye to accurately evaluate the visual performance of a display, as seen by a user. Read our new whitepaper, Enabling Display Measurement within Augmented & Virtual Reality Headsets, to learn more about the challenges of NED measurement, and how the unique optical design of Radiant’s AR/VR Lens solution is helping manufacturers ensure a great user experience.

CITATIONS:
- IDC’s Worldwide AR/VR Headset Tracker Taxonomy, 2017, published by International Data Corporation (IDC), March, 2017.
- Augmented/Virtual Reality Report Q1 2018, published by Digi-Capital, January 26, 2018
Join Mailing List
Stay up to date on our latest products, blog content, and events.
Join our Mailing List
